Introduction
The distinction between costs that remain constant regardless of changes in activity and sales volume and those that do not is known as the fixed cost vs. variable cost. Rent, salaries, and loan payments are examples of fixed costs that don't fluctuate with the volume of outputs. At the same time, direct labour, taxes, and operational expenses are examples of variable costs that alter directly and proportionally with the volume of business activity.
What Are Fixed and Variable Costs?
When manufacturing products or providing services, businesses face two primary categories of expenses: fixed costs and variable costs. A business's rent and loan payments are fixed costs over a specific period. In contrast, taxes, employee wages, and other operating expenses are variable costs that often fluctuate. Compared to variable expenses, fixed ones are simpler to anticipate, control, and allocate resources toward. As a company owner, you need to keep a close eye on and grasp the significance of both fixed and variable expenses since they dictate the pricing structure of your products and services.
Fixed Costs Example
Simply put, fixed costs don't fluctuate throughout a specific time frame. Expenses like rent and salaries tend to occur on a regular schedule. For instance, a small business owner can control one fixed Cost by negotiating with a landlord for an appropriate amount of rentable space. If a landlord leases out 10,000 square feet at $40 per square foot for ten years, the rent will be $40,000 per month for the duration of the lease, regardless of whether the business is profitable.
Variable Costs Example
To put it another way, when output is zero, so are the associated variable expenses. If we multiply the variable Cost per unit of output by the total quantity of output, we get the overall variable Cost for the business. Operations expenses that rise and fall with business volume are a classic case of variable costs. Increases in the price of utilities like electricity, gas, or water, or the salaries of temporary workers employed for specific projects, are examples of operating expenses that might plague a rapidly expanding company.
How Can a Business Reduce Variable Costs?
An organisation can cut its variable costs in several ways. For instance, if the quality of products is not compromised, increasing output while maintaining the same amount of material can significantly reduce expenses. Adopting new or enhanced technological processes or machinery may be a part of developing a new production process that can reduce variable costs. If this is not feasible, upper management may look for ways to save expenses by studying the process to find areas for efficiency and improvement.
Nature Of Cost
After a certain amount of time has passed, it shifts and changes.
It varies with the amount of output and is hence volume dependent.
How Are They Incurred?
Fixed expenses are those that must be paid regardless of the volume of output.
Expenditures for variable factors are directly proportional to the output volume.
Does It Change With The Number Of Units?
As the number of products made rises, the per-unit fixed costs fall.
No matter how many products are manufactured, variable costs will always be the same.
Impact On Profit
The more you produce, the less you spend, and the more money you'll make.
As long as costs are kept low, production rates won't affect profit margins.
Critical Differences Between Fixed Cost and Variable Cost
The following are crucial considerations when discussing the distinction between fixed and variable costs in economics:
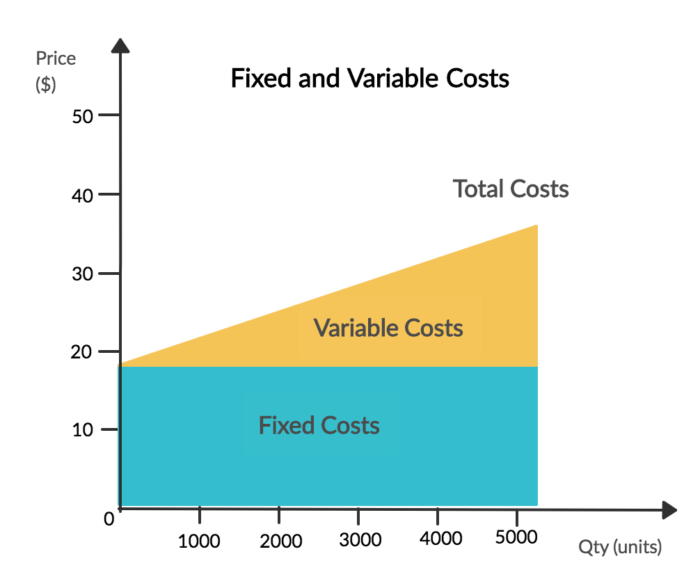
Unlike variable costs, fixed expenses don't fluctuate from one period to the next. In contrast to Variable Cost, which shifts in proportion to variations in output, Fixed Cost remains constant regardless of volume.
Unlike variable costs, fixed costs always exist, even if production is at a standstill. Variable Cost, on the other hand, is not fixed and will be incurred only when the business produces something.
The per-unit fixed Cost varies. Contrarily, variable costs are always the same per unit.
Knowing this distinction is essential for delving into a company's financials. Managers are more willing to accept low-priced offers for their products if the cost structure is predominantly made up of fixed costs (such as in an oil refinery). Most businesses in a given sector would have roughly the same cost structure and be required to generate sufficient revenue to pay their fixed expenses, which can increase the intensity of competition between them. After the initial fixed expenses are covered, the profit margin on further sales is usually relatively high. This indicates that a company with high fixed costs can reap enormous gains from a surge in sales but suffer similar losses from a fall in revenue.
Conclusion
Production expenses can be either variable or constant for a business. The product produced is directly related to the level of variable costs. Labor, commissions, and materials are all examples of variable expenses. Regardless matter how much or how little is produced, fixed costs will always be the same. These are fixed costs for leasing and renting payments, insurance premiums, and interest payments.